Wave Energy: A Bold Step into a Renewable Future on the Oregon Coast
The Oregon coast has long been synonymous with breathtaking landscapes and a rich maritime legacy, but today it is also emerging as a beacon of renewable energy innovation. Oregon State University’s groundbreaking PacWave testing facility promises to transform the region’s approach to sustainable power generation by harnessing the untapped potential of wave energy. As the facility nears its operational phase, key players such as the federal Bonneville Power Administration (BPA) are taking note, committing to purchase the clean, emissions-free electricity that this project aims to produce.
The prospect of generating power by tapping into the rhythm of the ocean waves might still seem like science fiction to some, but—with a blend of persistence and savvy technological advances—the idea is steadily evolving into a tangible reality. In our opinion, the PacWave initiative not only represents a huge leap for renewable energy on the Oregon coast but also exemplifies how partnerships between universities, government agencies, and private industry can stimulate new avenues of research, development, and economic growth.
Oregon State University’s PacWave Facility: Pioneering Wave Energy Progress
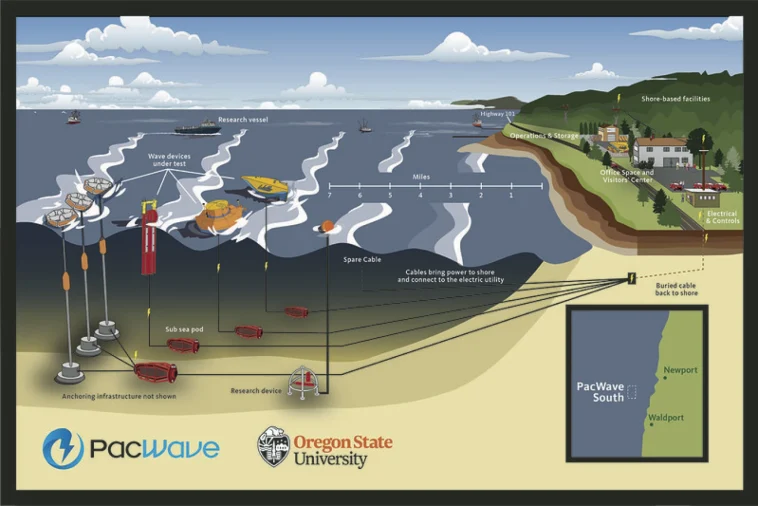
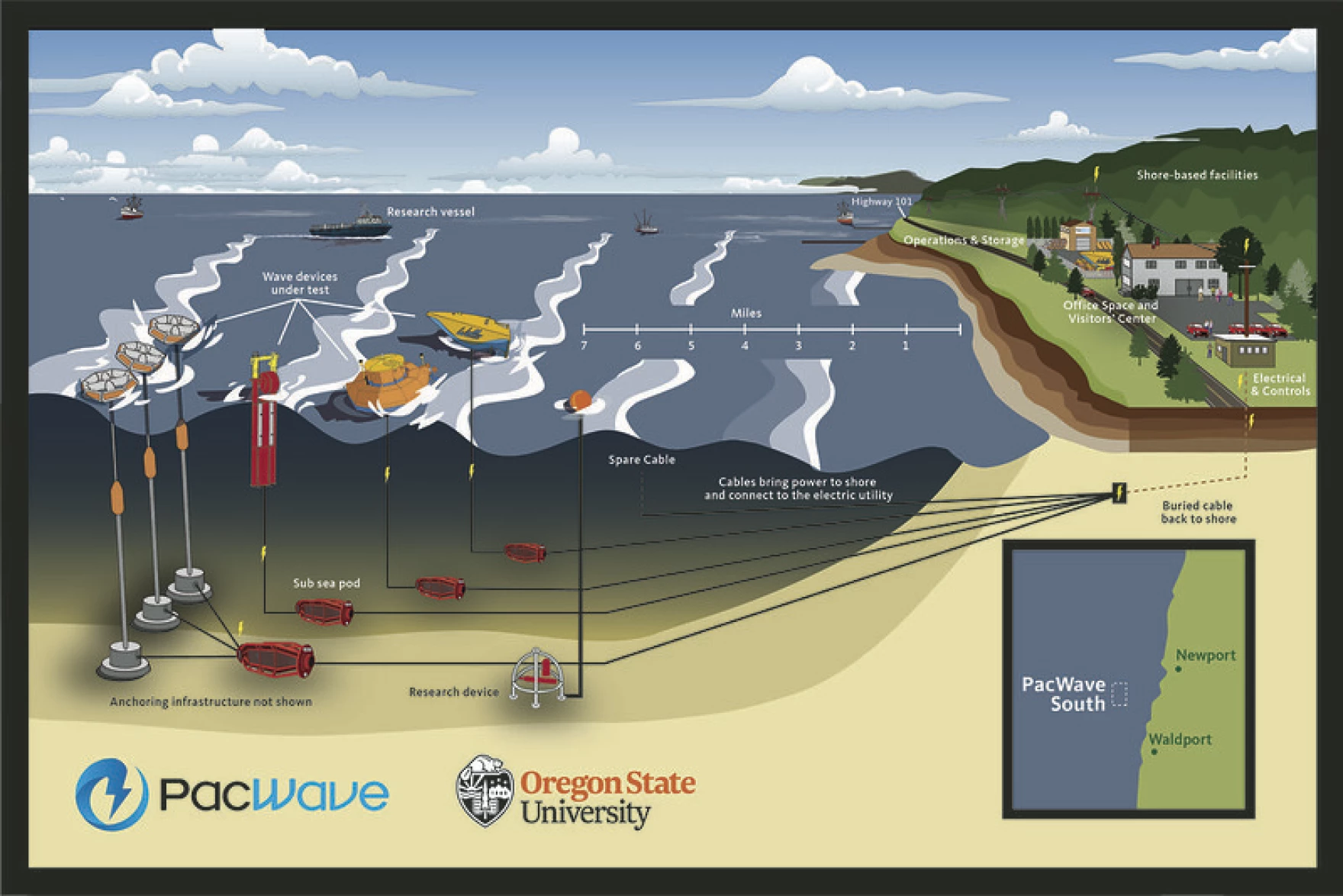
At the heart of this transformative project is Oregon State University’s PacWave testing facility, nestled off the coast of Newport. Developed in collaboration with the U.S. Department of Energy and the state of Oregon, this state-of-the-art facility is more than just a research station—it is a symbol of innovation. PacWave is designed to generate up to 20 megawatts of electricity per hour, a figure that, while ambitious, sets the stage for a future where wave energy becomes integral to the electricity grid.
Dan Hellin, the director of PacWave, expresses cautious optimism about the facility’s future output. While he concedes that the current phase of testing with emerging wave energy technology might not fully reach theoretical capacities, the presence of BPA as the sole purchaser of its clean energy is a significant vote of confidence. This partnership not only offers a revenue stream during the developmental stages but also sends a clear message to potential investors that the project has the necessary backing to push forward into commercial viability.
In many respects, PacWave is pioneering more than just technology—it’s setting a benchmark for collaborative innovation in renewable energy. Researchers and companies involved in this project are given a unique platform to test, refine, and eventually scale technologies that could revolutionize our approach to clean energy. The project serves as a living laboratory, where industry experts and academic researchers can work together to sort out the tricky parts and tangled issues that naturally arise when working with emerging technologies in a dynamic environment.
Bonneville Power Administration’s Commitment: Empowering Renewable Energy Initiatives
The role of the Bonneville Power Administration in this equation cannot be understated. As the largest power transmitter in the region, BPA’s decision to commit exclusively to purchasing the power generated by PacWave is both strategic and forward-thinking. By agreeing to buy all power output at a market rate determined by the Western Energy Imbalance Market, BPA provides the project with a dependable commercial outlet, reducing one of the nerve-racking uncertainties often associated with new energy ventures.
This approach fits within a broader strategy aimed at promoting renewable energy sources that move away from fossil fuel dependencies. In locking in a market rate for power generated, BPA is not only making a financial commitment but is also endorsing a vision where green energy stands alongside conventional forms of generation. Such support from a major player in the energy sector is essential when considering the delicate balance between innovation and the economic realities of developing new power sources.
BPA’s engagement with PacWave illustrates how institutional support from government-affiliated entities can lower barriers for adopting renewable energy. This is especially critical in sectors where the technology is still in its early, experimental stages. With BPA’s backing, the project can secure additional investment and funding, setting an example for future renewable endeavors that will need to find a path through the minor yet unavoidable twists and turns of new energy markets.
Overcoming Technical Hurdles and the Evolving Challenges of Wave Energy
Harnessing the power of ocean waves is filled with its own set of tricky parts and confusing bits. Unlike the relatively matured sectors of wind and solar power, wave energy remains in its infancy, with many involved in the industry working hard to figure a path through a landscape loaded with technical complications. The power devices designed to capture wave motion must contend with a dynamic and sometimes unpredictable environment, where the forces at play involve both steady rhythms and sudden, overwhelming surges.
The PacWave facility addresses some of these challenges by providing the infrastructure companies need to plug their devices into a broader network. Four subsea cables spanning about 50 miles each connect the wave energy converters in the ocean directly to onshore facilities, where the generated electricity can be monitored and managed. This system promises to transform the often nerve-racking process of transmitting energy from the sea to the grid into a more streamlined practice.
Yet, the field is still rife with complicated pieces that must be meticulously refined. For instance, researchers and engineers must ensure that these subsea connections can withstand the harsh ocean conditions. Moreover, the cutting-edge technology used to convert kinetic ocean energy into usable electrical power is still undergoing important trials. Every twist in this process, every little detail that requires fine-tuning, is a reminder of the substantial journey ahead before wave energy can join the ranks of its renewable counterparts on equal footing.
To clarify the core challenges, see the table below which outlines a few of the primary technical hurdles along with potential strategies to overcome them:
| Technical Challenge | Potential Strategy |
|---|---|
| Subsea Cable Durability | Implementing advanced materials and protective coatings |
| Energy Conversion Efficiency | Iterative testing and calibration of wave energy converters |
| Variable Wave Conditions | Developing adaptive response systems to accommodate changing conditions |
| Maintenance in Harsh Environments | Regular inspection and use of remote-operated vehicles |
Each of these points represents just a snippet of the myriad of issues that must be addressed, and while the path ahead is full of problems, the cumulative knowledge gained from these experiences is critical for progress.
Economic Implications for Local Communities and Investors in Coastal Renewable Energy
The economic prospects of the PacWave facility extend well beyond the immediate scope of renewable energy technology—they have significant ramifications for local communities and potential investors. When considered in tandem with regional development strategies, the project could act as a catalyst for a broader wave of economic change along the Oregon coast. By introducing a new revenue stream through clean energy generation, local governments and businesses may have greater ability to invest in infrastructure, education, and other community services.
In many respects, the project is a clear win-win scenario. Investors are presented with an opportunity to support a pioneering initiative that not only promotes sustainable energy but also offers potential long-term dividends as the technology matures. Meanwhile, the local workforce stands to benefit from job opportunities in the fields of engineering, marine technology, and renewable energy services, fostering a tighter integration between technological advancements and community economic development.
Key points regarding the economic impact include:
- Job creation in high-tech renewable energy sectors
- Growth in ancillary businesses related to maintenance, monitoring, and logistics
- Enhanced local investments due to increased reliability in alternative energy supply
- Potential for new public-private partnerships that accelerate further technological developments
These bullet points highlight how the economic ripple effects could extend far beyond the immediate facility, nurturing a stronger, more resilient economy in a rapidly evolving global energy sector. However, such integration is not free of its own set of complicated pieces, as investors and policymakers must work together to manage the challenges that surface along the way.
Government Support, Policy Dynamics, and Funding Reliance for New Energy Initiatives
Renewable energy initiatives such as the PacWave facility do not operate in isolation—they are deeply entwined with policy directions, government support, and the availability of funds. The project received a crucial green light from U.S. Energy Secretary Chris Wright earlier this year, which signified federal approval and laid a foundation for subsequent operational phases. Securing this level of support is especially important for sectors like wave energy, where many of the steps involved are both intimidating and replete with subtle details that can make or break a project’s success.
State and federal policies are often in a state of flux, with subtle shifts that can either encourage or hinder innovative renewable projects. The reliance on the U.S. Department of Energy for steady, reliable funding remains a central concern; as Hellin points out, the pace at which PacWave can truly take off depends on securing that funding and finding creative ways to manage every little twist in the path toward full operational capacity. For those pondering the future of wave energy, understanding these policy dynamics is as crucial as appreciating the technological aspects.
It is essential to consider the broader scope of government involvement, including:
- Ensuring sustained funding for research and development
- Crafting regulatory frameworks that address specific issues related to marine energy
- Offering tax incentives and other policy tools to stimulate private investment
- Providing a platform for collaboration between the public and private sectors
By taking a closer look at these elements, stakeholders can see that while the project does navigate some nerve-racking policy twists and turns, the overall direction is clearly set towards a commitment to renewable energy expansion. This not only benefits the environment but also contributes to a diversified and resilient energy portfolio for the future.
Sustainable Energy Breakthroughs on the Oregon Coast: Long-Term Prospects and Community Impact
Wave energy, in many respects, promises to be a game changer for sustainability efforts along the Oregon coastline. The continuous motion of the ocean provides a reliable, consistent source of power that could complement other renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar. As our energy needs evolve, embracing a variety of sources is not just a strategic move—it’s a critical one that might define the future of the region’s economic and environmental health.
From an environmental stand-point, the shift to clean energy sources is a super important step in reducing our carbon footprint and mitigating climate change. The PacWave facility stands at the intersection of technological innovation and environmental necessity, offering tangible hope that we can positively impact our ecosystem without compromising energy security. For local communities that have traditionally relied on conventional energy generation methods, transitioning to renewable energy sources could provide an added layer of long-term stability and prosperity.
Moreover, the project carries symbolic weight. It is not merely a test of technology; it is a public declaration that despite the many intimidating and overwhelming challenges of today’s energy landscape, there are viable, sustainable alternatives brewing in our own backyards. As coastal towns adapt to a future where clean energy is paramount, the integration of innovative projects like PacWave into everyday life may well lead to a ripple effect of further renewable initiatives.
Indicators of future benefits include:
- A reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and overall environmental improvement
- The stimulation of a local high-tech industry cluster, attractive to both talent and investment
- The development of a model that other coastal regions worldwide might replicate
- Enhanced community resilience through diversified energy portfolios
The long-term prospects for wave energy on the Oregon coast are optimistic, provided that today’s challenges are met with creative, collaborative solutions. The experimental phase is critical for gathering the kind of nuanced data that will guide future implementations, ensuring that every minute detail is accounted for and every twist in the journey is navigated with care.
Opportunities for Future Innovation in Coastal Energy Generation
Looking ahead, the opportunities arising from the PacWave facility extend far beyond immediate power generation. This initiative is part of a broader narrative where innovation meets environmental stewardship. Researchers and engineers are already brainstorming a range of possibilities to refine and build on today’s findings, including designing more resilient energy converters, improving the connectivity of subsea power transmission networks, and integrating advanced monitoring systems to optimize performance.
Future innovation may see wave energy not only become a competitive energy source but also evolve into a crucial component of smart grid systems. With further advancements, the technology could support energy storage solutions, integrate with other renewable technologies, and contribute to a decentralized energy landscape that is both flexible and reliable. The experiment being conducted at PacWave is a stepping stone—a test bed where ideas are put to the trial and every successful adaptation brings the vision of a sustainable, green energy future closer to reality.
There is also potential for economic innovation. The new technological developments spurred by the wave energy project could lead to spin-off companies and stimulate local tech ecosystems. Entrepreneurs and investors who have an eye on clean energy may find a wealth of opportunity in this emerging field, encouraging a broader culture of innovation throughout the region. The integration of new materials, digital monitoring, and even artificial intelligence to manage energy flow are areas that might see significant investment and research breakthroughs as the technology matures.
Below is a bulleted list summarizing potential areas for future innovation:
- Enhanced energy conversion systems with improved efficiency rates
- Developing smarter grid integration practices utilizing real-time data
- Innovative business models that bridge technology and market readiness
- Advanced subsea cabling solutions tailored for harsh marine environments
- Collaborative research initiatives that bring together academia, industry, and government
These investment opportunities and technological frontiers not only add excitement to the renewable energy sphere but also present a roadmap for future projects around the world. As wave energy technology evolves, there is little doubt that the lessons learned along the Oregon coast will resonate across other coastal regions eager to harness this natural resource.
Final Thoughts: Working Through the Tricky Parts in the Journey Toward a Green Energy Future
While the PacWave facility is a promising milestone, it is clear that the journey toward fully harnessing wave energy is loaded with issues, both technical and economic. In many ways, this endeavor exemplifies the dual realities of renewable energy innovation: on one side, there is the exhilarating prospect of a cleaner, brighter future; on the other, there is the ever-present challenge of sorting out complicated pieces and navigating through still-uncharted technical territory.
Working through these tricky parts requires more than just technological innovation – it requires persistent collaboration, dynamic government support, and a willingness among investors to take calculated risks. The role of BPA, along with supportive federal and state policies, helps to create a safety net that encourages private sector confidence, even as the process of testing and refinement continues.
Moreover, it is heartening to observe that initiatives like PacWave are already starting to pay dividends in the form of data, revenue, and an invigorated research community. As companies get into testing their devices at the facility and as innovative design tweaks are refined based on actual performance data, we get a clearer picture of how soon wave energy can potentially become cost competitive with more established forms of renewable energy. While wind and solar have already proven their economic viability, wave energy has its own story to tell—one that is just beginning to be written.
For local communities and policymakers, it is important to keep in mind that every bold step forward comes with its fair share of overwhelming challenges. But as we have seen time and again in the history of technological breakthroughs, perseverance coupled with thoughtful, collaborative action typically paves the way for success. The ongoing work at PacWave is not merely a test of engineering; it is also a test of our collective commitment to a sustainable future.
The road ahead will undoubtedly be marked by both small victories and setbacks. Each small twist, every nerve-racking setback, and each fine detail that needs ironing out is part of a grand experiment that could redefine the energy landscape of not just Oregon, but potentially the entire nation. As the research community dives in and continues to poke around at the hidden complexities of wave energy technology, there is genuine optimism that these efforts will eventually lead to more efficient, reliable methods of generating power from the ocean’s relentless motion.
In conclusion, the PacWave initiative stands as a testament to what can be achieved when forward-thinking institutions, dedicated researchers, and strategic governmental partners come together to tackle the complications of renewable energy head-on. Though the path may wind through intimidating challenges and full-of-problems policy debates, the potential rewards are enormous: a cleaner environment, more robust local economies, and a renewable energy system that truly meets the needs of tomorrow.
As we watch this project develop and mature, we must acknowledge that every innovation in the realm of renewable energy starts with tentative, experimental phases. Today’s prototype and experimental phase is the seedbed from which a future of sustainable and economically viable energy generation will grow. The Oregon coast, long celebrated for its natural beauty, may soon also be recognized as a hub for cutting-edge technological innovation—a place where the mighty power of the ocean is transformed into a source of clean, reliable energy.
For investors, policymakers, and community stakeholders alike, the PacWave facility offers much more than just a glimpse of the future—it provides a working model, a field test, and a call to action. It reminds us that while the journey toward broad adoption of wave energy is filled with tangled issues and overwhelming challenges, the rewards of persistence are tremendous. By embracing the experimental process and learning to steer through the inevitable twists and turns, we pave the way for a renewable future that could redefine how we power our world.
Ultimately, if we are to truly meet the needs of a changing world and a shifting energy landscape, our approach must be as dynamic and resilient as the forces of nature we seek to harness. Oregon State University’s PacWave facility, in partnership with BPA and other stakeholders, is charting a course through the tricky parts, providing an invaluable test space for technologies that might one day become the backbone of our renewable energy infrastructure. This is a journey not marked by immediate perfection but by gradual, steady progress—a journey toward a future where the power of the ocean is as instrumental in lighting our homes and driving our industries as it is in shaping the natural beauty of our coastal regions.
In the end, the story of PacWave is a story of hope, innovation, and the relentless pursuit of a sustainable future. It is a reminder that while every new endeavor may be riddled with tension and complicated pieces, it is through collaboration, perseverance, and a willingness to take risks that we truly make our way toward a cleaner, brighter, and more sustainable tomorrow.
Originally Post From https://www.klcc.org/politics-government/2025-09-30/bpa-will-get-power-of-wave-energy-harnessed-at-oregon-state-university-test-site
Read more about this topic at
Wave power – U.S. Energy Information Administration …
A brief history of wave energy: Harnessing ocean power